Sailing the fields –
The ship is one of only a handful of such graves ever found mostly intact in Norway.
Ground-penetrating radar recently revealed a Viking Age ship hidden beneath the topsoil of a farm near the former town of Edøy in western Norway. The ship would have held the body of an ancient Norse leader along with weapons, loot, and other items. Nearby, the remains of postholes mark the ghostly outlines of two longhouses. The find could offer a wealth of information about ancient shipbuilding and Norse burial rites.
A forgotten grave
The outline of the ship shows up clearly in the radar images, circled by the remains of a ditch that once surrounded a burial mound. “This is a very common trait for grave mounds,” archaeologist Dag-Øyvind Solem, of the Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU), told Ars. “In addition to having a potentially symbolic meaning, it is thought that [ditches] have the very practical function of making the mounds seem bigger than they really were.”
Farmers’ plows destroyed the burial mound centuries ago, and soil eventually filled in the surrounding ditch. But that looser soil holds more moisture than the adjacent ground and reflect radar differently. In radar images, the result is an accidentally perfect logo for Viking Age archeology: the hull of a ship in a circle. The largest Norse ship burial ever found — the Gjellestad ship — stood out in a 2018 radar survey with the same distinctive outline.
Both ends of the ship seem to have suffered damage, probably from a thousand years’ worth of plowing. But most of the hull seems intact. The radar images are detailed enough for archaeologists to recognize the keel (a long wooden timber that forms the backbone of a ship) and the first two planks on either side. Based on the length of the keel, the ship was probably between 16 and (meters) 52 to (feet (long.)
The find was a stroke of luck, since the site wasn’t even in the team’s original survey area. “We had actually finished the agreed-upon area, but we had time to spare and decided to do a quick survey over another field,” archaeologist Manuel Gabler of NIKU said in a press release. “It turned out to be a good decision.”
It probably came as a surprise to farmer Per Hassle, too, but he’s taking the discovery in stride. “The burial is indeed located on a working farm, but we couldn’t have wished for a more agreeable landowner,” Solem told Ars. “He is very interested in history, especially local history, and is very enthusiastic about the project.”
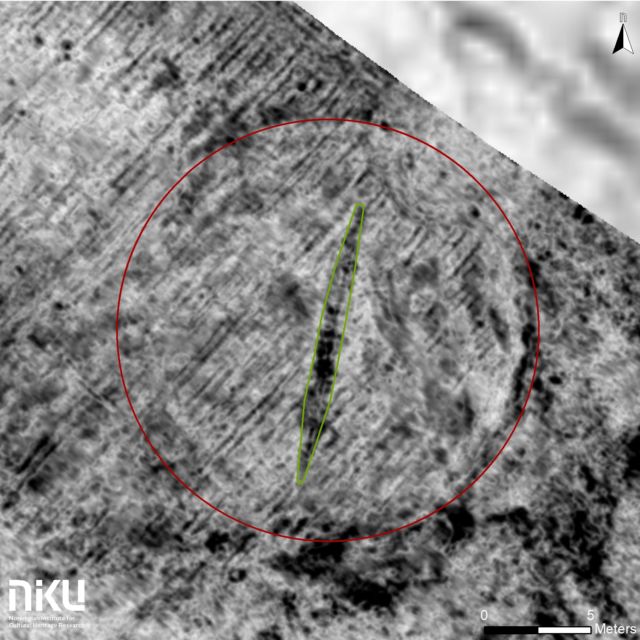
Enlarge/This aerial radar image shows the buried ship, surrounded by traces of a ditch.
The mysteries in Per Hassle’s field
At this point, Solem and his colleagues don’t know whose grave this is or how many skeletons it contains. It almost certainly belonged to a ruler or another very powerful person, though. A ship unearthed in the 1880 s at the Gokstad site in southern Norway contained the bones of one man, but occasionally the deceased also hauled a slave or family member along to the afterlife. And the Oseberg ship, unearthed in southern Norway in the early 1900 s, contained the bodies of two women, surrounded by elaborately carved sleighs, carts, and other artifacts.
Archaeologists aren’t sure whether weapons, jewelry, and other grave goods also lie buried beneath the farm. When 19 th-century archaeologists unearthed the Gokstad ship, it had apparently already been looted. Although the kind of person who rated a ship burial would usually have been interred with weapons, gold, and silver artifacts, archaeologists found none. It’s possible that the same fate has already befallen the Edøy burial, but only further fieldwork will tell.
And there’s no way to tell exactly how old the ship is, although it must be at least a thousand years old, dating either to the Viking Age or the even older Merovingian period which preceded it. The same goes for the longhouses, which may or not be from the same time period as the ship.
“What we can say is that this kind of house usually dates to the pre-Christian period in Norway,” Solem told Ars. “In some cases, houses have been found within burial sites that have been interpreted as ‘death houses,’ that is, houses that probably were connected to the cult of the dead.”
Not the only recent discovery
Because such extravagant burials were reserved for rulers or other elites, and because many burial mounds have been plowed flat, archaeologists have only found a handful in Norway, along with a few others elsewhere in Northern Europe.
Last year, another aerial radar survey in southeastern Norway found a 20 – meter-long ship buried just half a meter beneath a field at a site called Gjellestad. Archaeologists from NIKU excavated a small area of the ship during summer 2019; they found the keel mostly intact, but many of the ship’s other timbers had long since rotted away. But a modern pipeline had damaged that portion of the grave, so it’s possible that other areas of the ship are in better shape. The archaeologists took wood samples but haven’t released any results so far.
“The dating of the ship is not public yet, but as it seems to have some of the same traits as the Edøy ship, we suspect this too might be shortly pre-dating the Viking period, “Solem told Ars.
The future of the buried ship
Meanwhile at Edøy, Solem and his colleagues hope to conduct more radar surveys before they, too, excavate a small trench at the site. “Different types of georadar applied at different times of the year will hopefully lead to an optimal image of the ship itself, to try to see as many details of the ship as possible,” he told Ars. “We also would like to do this in a larger area around the ship.”
Excavating a small area of the buried ship will give the archaeologists a better look at what condition it’s in, and they’ll be able to take wood samples for dating and other analysis. Eventually, they hope to answer questions about an important development in early medieval technology: the keel.
“The evolution of the keel, which contributed to the beginning of the Viking period, is an important subject in Scandinavia,” Solem told Ars . “A find like this will hopefully contribute to our understanding of the Viking ship development.”
But for now, the future of the Edøy ship, and those questions, isn’t settled. “The decision of what will happen next is up to the Directorate of Cultural Heritage (Riksantikvaren),” explained Solem. “To be frank, we don’t know whether the find will be fully excavated or even left wholly alone.”
Listing image byManuel Gabler, NIKU







GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings