
Introduction: According to statistics from cybersecurity companies, more and more companies are refusing to pay ransoms to ransomware gangs.
According to statistics from cybersecurity companies, more and more companies are refusing to pay ransoms to ransomware gangs, with the number of companies paying ransoms reaching a record low of only 28% in the first quarter of 2024.
It was 29% in Q4 2023. The number of businesses willing to pay ransomware groups has been declining since the beginning of 2019.
This decline is due to more advanced protection measures by enterprises and a lack of integrity caused by cybercriminals' repeated violations of promises not to release or resell stolen data if a ransom is paid.
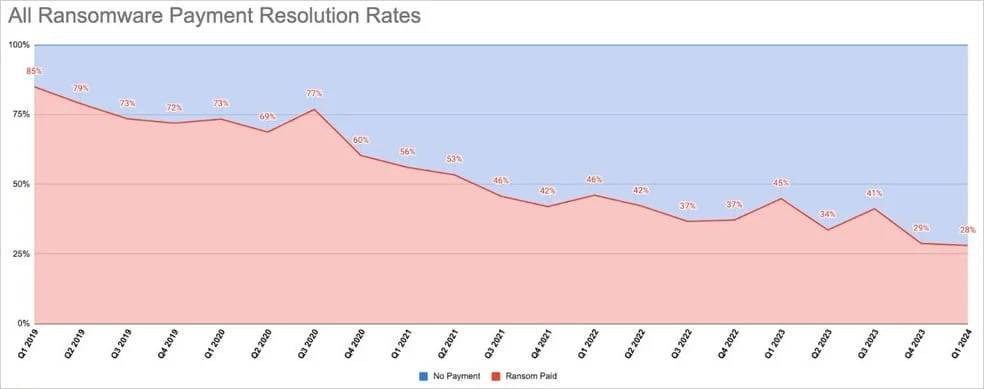
Ransom payment rates in recent years
However, it’s worth noting that despite the drop in payout rates, amounts paid to ransomware groups are higher than ever, reaching $1.1 billion last year, according to a Chainaanalysis report.
This is due to ransomware gangs targeting more businesses by increasing the frequency of attacks and demanding more specific numbers to prevent leaks of stolen secrets and provide victims with decryption keys.
Coveware reported that in the first quarter of 2024, the average ransom amount decreased by 32% quarter-on-quarter and is currently $381,980, while the median ransom amount increased by 25% quarter-over-quarter to $250,000.
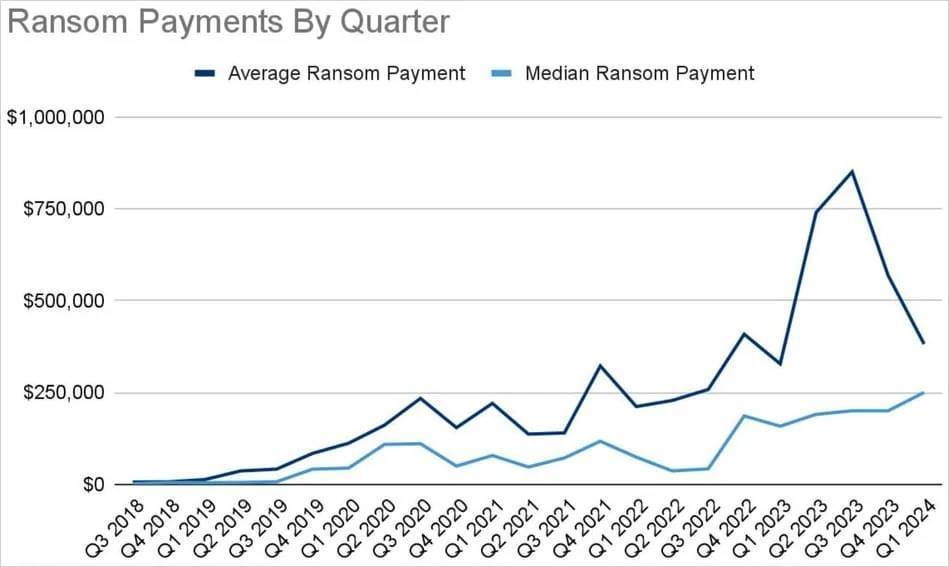
Payment amount trends
The decrease in the average ransom amount and the increase in the median ransom amount indicate a decrease in high-value ransoms and an increase in moderate amounts. This could be due to ransom demands becoming more modest or fewer high-value targets for extortion.
Regarding the initial infiltration method, the number of unknown cases continues to increase, reaching nearly half of all reported cases in the first quarter of 2024.
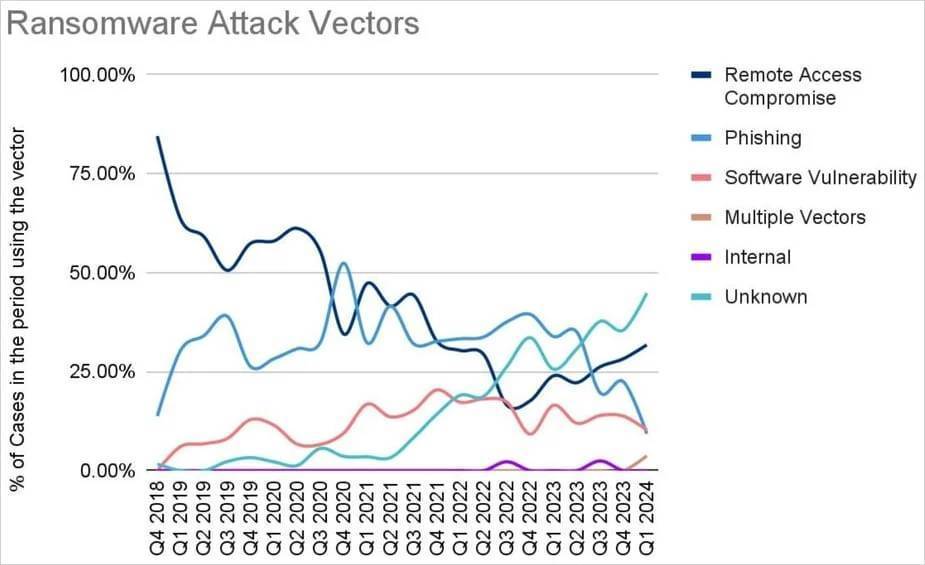
Ransomware attack vectors
From the identified vulnerabilities, remote access and vulnerability exploitation played the largest role, with CVE-2023-20269, CVE-2023-4966 and CVE-2024-1708-9 flaws being exploited by ransomware operators in the first quarter The most widespread.
Law enforcement effect
Coveware reports that the FBI's LockBit breach had a huge impact on cyber-hacking operations, as reflected in their attack statistics, which also led to payment disputes and more, as seen with BlackCat/ALPHV.
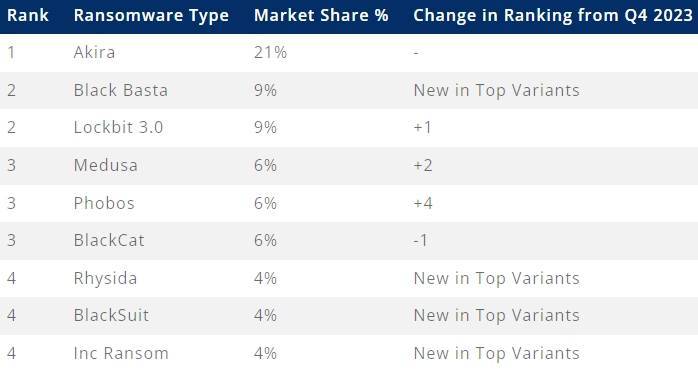
Most active ransomware groups in Q1 2024
Additionally, these enforcement actions eroded the confidence of other ransomware affiliates in RaaS operators, with many deciding to operate independently.
“The Babuk fork has increased in recent attacks, and several former RaaS affiliates are using the nearly free Dharma/Phobos service,” Coveware explained in the report.
According to the security company, in many cases its affiliates decided to stop cybercrime entirely.
Most players in the cyber extortion ecosystem are not hardened criminals but individuals with STEM skills who live in jurisdictions that lack extradition treaties and don’t have many legitimate economic opportunities to apply their skills.
In this space, Akira topped the list of the most active ransomware in terms of attacks launched in the first quarter of this year, a position it has held for nine consecutive months. The FBI reported that Akira collected $42 million in ransoms and was responsible for breaches at at least 250 businesses.
Article translated from: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/ransomware-payments-drop-to-record-low-of-28-percent-in-q1-2024/ If reprinted, please indicate the original address


Thank you for your support, I will continue to work hard!
OpenWeChatScan and click on the upper right corner to share.
You may be interested
-

All-time low! Ransomware payments drop to 28% in Q1 2024
-

Review of Security Dynamics | The Cyberspace Administration of China has deployed the special operation “Clear and Combat Illegal Information External Links”. The APT28 hacker group uses Windows vulnerabilities to conduct network attacks.
-

Hackers use old version of Microsoft Office 0 day to implement Cobalt Strike
-

Security Update Review | UnitedHealth Group pays ransom to ransomware gang to stop data breach, Microsoft fixes Outlook security alert bug
-

More than 5,000 CrushFTP servers were attacked by zero-day vulnerabilities
-

GitLab affected by GitHub-style CDN flaw that allowed malware to be hosted











GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings